After the basics of Regression, it’s time for basics of Classification. And, what can be easier than Logistic Regression!
This is what Classification actually means:
We saved the easy algorithms for the last. Happy Learning. :)
Fear is the enemy of logic.
What is Logistic Regression?
It’s a classification algorithm, that is used where the response variable is categorical. The idea of Logistic Regression is to find a relationship between features and probability of particular outcome.
E.g. When we have to predict if a student passes or fails in an exam when the number of hours spent studying is given as a feature, the response variable has two values, pass and fail.
This type of a problem is referred to as Binomial Logistic Regression, where the response variable has two values 0 and 1 or pass and fail or true and false. Multinomial Logistic Regression deals with situations where the response variable can have three or more possible values.
Why Logistic, not Linear?
With binary classification, let ‘x’ be some feature and ‘y’ be the output which can be either 0 or 1. The probability that the output is 1 given its input can be represented as:
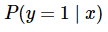
If we predict the probability via linear regression, we can state it as:
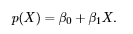
Linear regression model can generate the predicted probability as any number ranging from negative to positive infinity, whereas probability of an outcome can only lie between 0< P(x)<1.
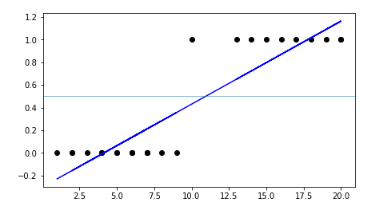
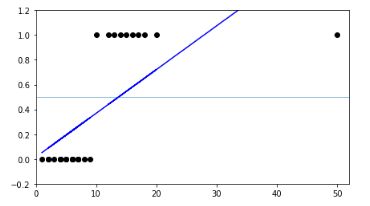
Also, Linear regression has a considerable effect on outliers. To avoid this problem, log-odds function or logit function is used.
Logit Function
Logistic regression can be expressed as:
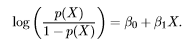
where, the left hand side is called the logit or log-odds function, and p(x)/(1-p(x)) is called odds.
The odds signifies the ratio of probability of success to probability of failure. Therefore, in Logistic Regression, linear combination of inputs are mapped to the log(odds) - the output being equal to 1. If we take an inverse of the above function, we get:
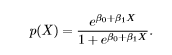
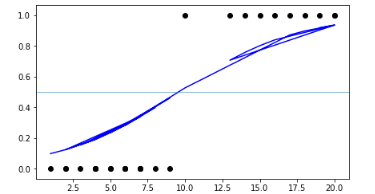
This is known as the Sigmoid function and it gives an S-shaped curve. It always gives a value of probability ranging from 0<p<1.
Estimation of Regression Coefficients
Unlike linear regression model, that uses Ordinary Least Square for parameter estimation, we use Maximum Likelihood Estimation. There can be infinite sets of regression coefficients. The maximum likelihood estimate is that set of regression coefficients for which the probability of getting the data we have observed is maximum. If we have binary data, the probability of each outcome is simply π if it was a success, and 1−π otherwise. Therefore we have the likelihood function:
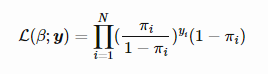
To determine the value of parameters, log of likelihood function is taken, since it does not change the properties of the function. The log-likelihood is differentiated and using iterative techniques like Newton method, values of parameters that maximise the log-likelihood are determined.
Performance of Logistic Regression model:
To evaluate the performance of a logistic regression model, Deviance is used in lieu of sum of squares calculations.
-
Null Deviance indicates the response predicted by a model with nothing but an intercept.
-
Model deviance indicates the response predicted by a model on adding independent variables. If the model deviance is significantly smaller than the null deviance, one can conclude that the parameter or set of parameters significantly improved model fit.
-
Another way to find the accuracy of model is by using Confusion Matrix.
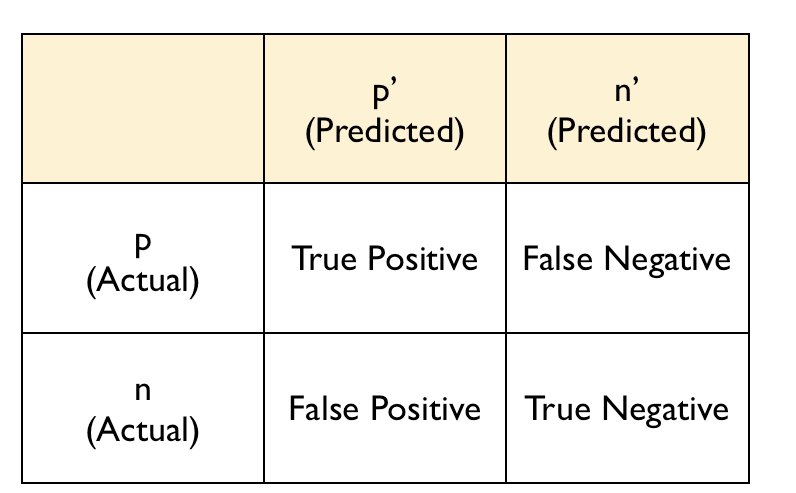
The accuracy of the model is given by:

Multi-class Logistic Regression
The basic intuition behind Multi-class and binary Logistic regression is same. However, for multi-class problem we follow a one v/s all approach.
Eg. If we have to predict whether the weather is sunny, rainy, or windy, we are dealing with a Multi-class problem. We turn this problem into three binary classification problem i.e whether it is sunny or not, whether it is rainy or not and whether it is windy or not. We run all three classifications independently on input. The classification for which the value of probability is maximum relative to others, is the solution.

Is it really that good?
As simple it seems, does it even solve any purpose? Let’s check!
Pros
-
Simple and efficient.
-
Low variance.
-
It provides probability score for observations.
Cons:
-
Doesn’t handle large number of categorical features/variables well.
-
It requires transformation of non-linear features.
Implementation in Python
I applied the model on the data set of Tic-tac-toe game. This database encodes the complete set of possible board configurations at the end of tic-tac-toe games, where x is assumed to have played first. The target concept is win for x i.e., when x has one of 8 possible ways to create a “three-in-a-row” sequence.
Click HERE for the full code. Anybody can code, trust me!
References
Footnotes
You are aware of the most common ML Algorithms in the industry by now. I am thankful to all of you for being with us all this while. Wait for the last one!
Thanks for reading. :) And, ❤ if this was a good read. Enjoy!
Editor: Akhil Gupta
